Unit 8
Phrase Structures
Step 1
Notes
Melody & Phrase:
Forms can begin at the beginning of a composition, and they usually end at the conclusion of a cadence
Smallest melodic unit is called a motive, and 2 motives combine to make-up a phrase
Phrase is a set of notes that combine to make a musical sentence, which leads to a cadence.
A pause in the middle of a phrase usually indicates the end of a motive.
The phrase is the smallest type of form and can be made up of any # of measures (standard is 4)
Antecedent ends with half cadence of imperfect authentic cadence
Consequent ends with a perfect authentic cadence
Everything You Wanted to Know About Phrases:
Sequence: Two or more appearances of the motive, must be transposed
Period: Two phrases in which the antecedent promises a continuation and the consequent provides a conclusive cadence
Symmetrical Period: A period whose antecedent and consequent phrases are of the same or similar length.
Asymmetrical Period: A period whose antecedent and consequent phrases are of different lengths.
Parallel Period: A symmetrical period whose antecedent and consequent phrases are similar in content.
Contrasting Period: A period whose antecedent and consequent phrases are dissimilar.
Phrase Group: 3 or more phrases, at least 2 are similar, only the last ends with a conclusive cadence.
Phrase Chain: 3 or more dissimilar phrases, only the last ends with a conclusive cadence.
Phrase Link: A melodic/rhythmic device used to link grouped phrases, showing that a period, phrase group, or phrase chain has not yet reached its conclusion.
Phrase Elision: when the cadence of one phrase occurs simultaneously with the beginning of the next phrase.
Phrase Member: Short melodic unit that makes up a portion of a phrase, contains several motives
Motive: Short melodic figure used as a constructional element, the smallest structure from which additional material may be created. Must appear at least twice, but doesn't need to be exactly the same
Repetition: A motive repeated
Imitation: A motive repeated in a different voice
Transposition: A motive repeated starting on a different pitch than the original
- Real Transposition: The interval structure of the motive is the same
- Tonal Transposition: Interval structure of the motive is the same, but the quality of the intervals may be different
LOTR Leitmotifs:
Leitmotif:A piece for a specific character/group/thing
Adding more instruments and variations of the piece at different parts in a film
Also remove instruments as it moves on, changes tempo and harmonies as well
Step 2
Is the antecedent phrase symmetrical or asymmetrical to the consequent
phrase?
Symmetrical
Is the antecedent phrase similar or contrasting to the consequent phrase?
Similar
Step 3
Is the antecedent phrase symmetrical or asymmetrical to the consequent
phrase?
Asymmetrical
Is the antecedent phrase similar or contrasting to the consequent phrase?
Contrasting
What kind of cadence is represented at the end of the antecedent phrase?
Imperfect Authentic Cadence
What kind of cadence is represented at the end of the consequent phrase?
Deceptive Cadence
Finale Project/Summative Assessment
Step 1

Textures
Step 1
Notes:
Textures Defined:
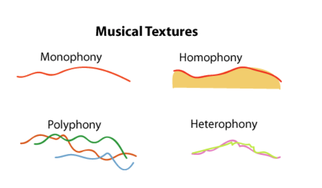
Texture is how much is going on in the music at any given moment
Monophonic music has only 1 melodic line, with no harmony or counterpoint
May have rhythmic accompaniment, but only 1 line that has specific pitches
Heterophonic: rare in Western music
There is only one melody, but different variations of it are being sung or played at the same time
Middle Eastern, South Asian, and Native American music traditions
Textures Examples:
Biphonic: 2 distinct lines, the lower sustaining a drone/constant pitch, while the other line creates a more elaborate melody above it
ex: Pedal Tones
Monophonic: music with one melody line, with no harmony or counterpoint.
Homophonic: one clear melody line where all other parts fill in the chords. It is clear they are not their own melody part and are there to support and have the same rhythm as the melody or fill in the chords.
Chords, accompaniment, harmony, or harmonies
Can sound very different, but when played with the harmony it is clear they are not independent melodies
Polyphonic: more than one melody is occurring at the same time.
Rounds, canons, and fugues
Step 2
Texture clues by sight
Texture clues by sound
Musical texture is describing how much is going on in music at any given moment. Monophony (mono = one) has only one melodic line going on with no harmony or counterpoint. Homophony (homo = similar, same) has one distinctive melodic line and other parts filling in the parts of the chord. Polyphony (poly = many) is when more than one melody is occurring at the same time. Lastly, Heterophony (hetero = different) is when there is one melody, but different variations are being sung/played at the same time.
Finale Project/Summative Assessment

Song Forms
Step 1
Unit 18
Step 2
Would you describe the form of America as being binary or ternary? Explain your answer.
Binary, since it only shows 2 sections and does not have a restatement of the A section. It would be ternary if the A section was restated after the B section.
Would you describe the form of Swing Low Sweet Chariot as being binary or ternary? Explain your answer.
Ternary, since there is a restatement of the A section, creating 3 sections. If the 3rd section was not there and not a restatement of the first section, it would be binary.
Summative Assessment
Step 1
Use the 3rd
Movement Autumn from Vivaldi's Four Seasons to provide the Letter Code that symbolizes the
form
ABACADAEAFAGA
Step 2
Use Little
Fugue in G by J.S. Bach to provide the # of times the subject is heard in it's
main form
7 times
 Getting Started
Getting Started